A Watched Pot Never Boils: Still Waiting on Margin Relief
As expected after lackluster job gains in May, the Federal Open Market Committee declined to raise the Fed Funds target at the latest policy meeting on June 15th. While the majority of policymakers still expect the Fed to boost rates twice before the end of this year, the number of officials who forecast just one rate hike increased from one to six from the previous forecasting round in March. In addition, Fed officials lowered their expectations for future years, now expecting the fed funds rate to rise to 1.6% by year-end 2017, down from the 1.9% estimate in March, and 2.4% in 2018, down from the previous estimate of 3.0%. During a press briefing on June 3rd, members of the Economic Advisory Committee of the American Bankers Association said they still expect the Fed to boost rates twice before the end of this year, but after years of speculation regarding timing of rate increases, when that will happen remains anyone’s best guess. The bond market never believed the forecasts.
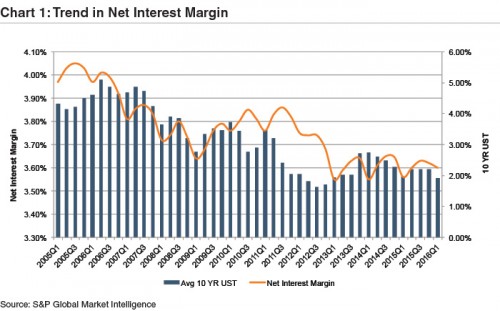
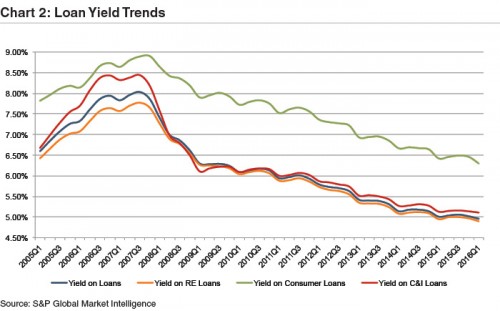
Rate increases are long awaited by community bankers as banks are facing profitability challenges. Net interest margins continue to compress and loan growth remains stymied by intense competition for high quality loans. Margin relief remains out of the grasp of most community banks, absent further rate hikes beyond the December 2015 hike. After rebounding modestly in the third and fourth quarter of 2015, the median net interest margin of community banks (defined as those with assets between $100 million and $5 billion), ticked down modestly in the first quarter of 2016 as intense competition for quality loans drove down loan yields and the decline in long-term rates put downward pressure on securities’ yields (Charts 1 and 2).
Overall, median net interest income continued to increase as growth in loans offset margin compression, but intense competition raises concerns over how much credit standards have been relaxed to drive loan growth.
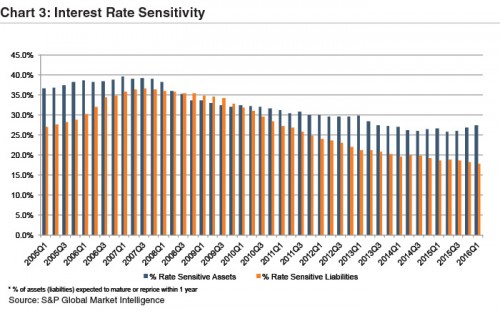
Although the majority of banks’ balance sheets are poised to take advantage of rising rates, the lift to net interest margins is dependent on asset yields rising faster than the cost of funds (Chart 3).
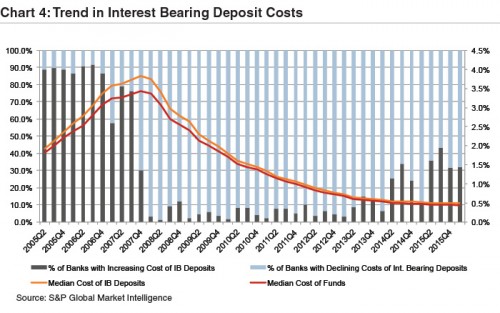
While deposits costs essentially reached a floor several quarters ago, data suggests the threat of rising deposit rates may limit margin expansion in a rising rate environment. As shown in Chart 4, the percentage of banks reporting quarter-over-quarter increases in the cost of interest bearing deposits has been trending upward over the last eight quarters. In a higher rate environment, customers are more likely to shop around for higher rates. The increase observed in interest bearing accounts could reflect the fact that higher loan growth has compelled some banks to raise rates or perhaps an effort to build goodwill with customers in anticipation of rising rates and increased rate sensitivity. For banks with asset sensitive balance sheets, the benefit of rising interest rates will be greater the stickier low cost deposits are.
While net interest margin is a key metric for banks, focusing on other drivers of profitability is one way to combat margin compression in the face of further delays in interest rate hikes or upward pressure on deposit costs. Consider the following:
- Look for opportunities to grow non-interest income. One strategic option may be to expand bank offerings into non-traditional bank business lines that are less capital intensive and offer prospects for non-interest income growth such as acquisitions or partnerships with insurance, wealth management, specialty finance, and/or financial technology companies. FinTech’s consumer-focused technology and ability to quickly adapt can pair well with community banks who can provide an established customer base and knowledge of the regulatory process and environment. For more information, we recently wrote an article on why current market conditions may be ripe for FinTech partnerships.
- Leverage technology to curb efficiency ratios. Compliance and regulatory costs continue to rise and represent a bigger burden to community banks who lack the scale to accommodate these expenses in comparison to their larger peers. A recent article from American Banker included data presented by Chris Nichols, chief strategy officer of CenterState Banks, at a recent fintech conference in Atlanta that shows why engaging customers digitally is more efficient. Furthermore, a recent article published on SNL highlights how, in some regards, community banks can be quicker to adopt new technology than larger peers. While size may limit what projects are feasible for community banks, agility has its benefits.
- Increase scale. Create economies of scale and improve profitability organically or by merging with a larger company. Organic loan growth is an obvious cure to the margin blues, but must be achieved while maintaining credit quality and holding adequate capital. M&A remains a classic solution to revenue headwinds in a mature industry, and bank acquirers can potentially have savings beyond expense synergies with some NIM relief resulting from potential accretion income on the acquired assets, which are marked to fair value at acquisition.
Mercer Capital has a long history of working with banks and helping to solve complex problems ranging from valuation issues to considering different strategic options. If you would like to discuss your bank’s unique situation in confidence, feel free to contact us.