The Role of Earn-Outs in RIA Transactions (Part Three)
In last week’s blog post, we covered five considerations for designing earn-outs. To recap, these considerations are as follows:
- Defining the continuing business that will be the subject of the earn-out
- Determining the appropriate period for the earn-out
- Determining to what extent the buyer will assist or impede the seller’s performance during the earn-out period
- Defining what performance metrics will control the earn-out payment(s)
- Determining other earn-out features (caps on payments, clawbacks, etc.)
While there is no one set of rules for structuring an earn-out, keeping these conceptual issues in mind can help anchor the negotiation. This week, we look at an example RIA transaction to illustrate how these considerations come into play when buyers and sellers are working out deal pricing and structure.
RIA Transaction Example
Consider the example of a depository institution, Hypothetical Savings Bank (HSB). HSB has a substantial lending platform, but it also has a trust department that operates as something of an afterthought. HSB’s senior executives consider options for closing or somehow spinning off the trust operation, but because of customer overlap, lengthy trust officer tenure with the bank, and concerns by major shareholders who need fiduciary services, HSB instead hopes to bolster the profitability of trust operations by acquiring an RIA.
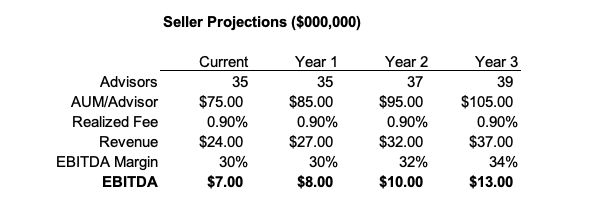
Following a search, HSB settles on Typical Wealth Management (TWM). TWM has 35 advisors and combined discretionary assets under management of $2.6 billion (an average of $75 million per advisor). TWM has a fifteen-year track record of consistent growth, but with the founding generation nearing retirement age, the firm needs a new home for its clients and advisors.
The Seller’s Perspective
TWM’s founders are motivated, but not compelled, to sell the firm. TWM generates 90 basis points of realized fees per dollar of AUM and a 30% EBITDA margin. Even after paying executives and advisors, TWM makes $7MM of EBITDA per year, and the founders know that profitability has significant financial value to HSB, in addition to providing strategic cover to shore up the trust department.
Further, Typical Wealth Management has experienced considerable growth in recent years, and believes it can credibly extend that growth into the future, adding advisors, clients, and taking advantage of the upward drift in financial markets to improve revenue and enhance margins.
Given what it represents to be very conservative projections, and which don’t take into account any cross-selling from the bank or potential fee enhancements (TWM believes it charges below-market fees to some clients), the seller wants 12x run rate EBITDA, or about $85 million, noting that this is only about 10x forward EBITDA, and less than 7x EBITDA three years hence.
The Buyer’s Perspective
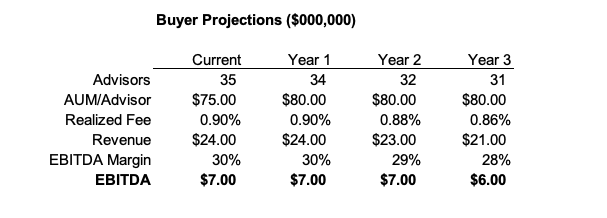
The commercial bankers at HSB are not overly familiar with the wealth management industry, but they know banks rarely double profitability in three years and suspect they’ll have a tough time convincing their board to pay top dollar for something without tangible book value.
Bank culture and investment management do not always mix well, and HSB worries whether TWM’s clients will stay if TWM’s senior staff starts to retire. Further, they wonder if TWM’s fee schedule is sustainable in an era of ETFs and robo-advisors. They create a much less sanguine projection to model their possible downside.
Based on this, HSB management wants to offer about $40 million for TWM, which is about six times run rate EBITDA. This pricing gives the seller some credit for the recurring nature of the revenue stream, but doesn’t pay for growth that may or may not happen following a change of control transaction.
The Compromise
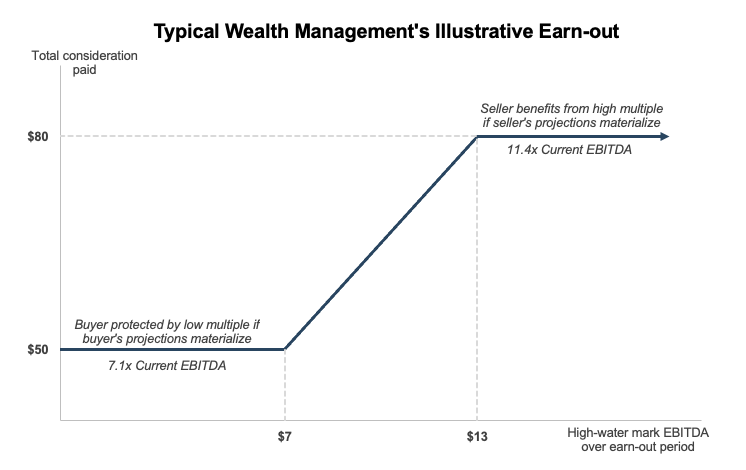
With a bid/ask spread of $45 million, the advisors for both buyer and seller know that a deal isn’t possible unless one or both parties is willing to move off of their expectations significantly (unlikely) or a mechanism is devised to reward the seller in the event of excellent performance and protect the buyer if performance is lackluster. Even though the buyer is cautious about overpaying, they eventually agree to a stronger multiple on current performance and offer $50 million up front for TWM. The rest of the payment, if any, will come from an earn-out. Contingent consideration of as much as $30 million is negotiated with the following features:
- TWM will be rebranded as Hypothetical Wealth Management, but the enterprise will be run as a separate division of the bank during the term of the earn-out. This division will not pay any overhead charge to the bank, except as specifically designated for marketing projects through the bank that are managed by the senior principals of the wealth management division. As a consequence, the sellers will be able to maintain control over their performance and their overhead structure during the term of the earn-out.
- The earn-out period is negotiated to the last three years. Both buyer and seller agree that, in a three year period, the value delivered to the seller will become evident.
- Buyer and seller agree to modest credits if, for example, the RIA recommends a client develop a fiduciary relationship with the bank’s trust department, or if the bank’s trust department refers a wealth management prospect to the RIA. Nevertheless, in order to keep matters simple during the term of the earn-out, both parties agree to manage their operations separately while the bank determines whether or not the wealth management division can continue to market and grow as an extension of the bank’s brand.
- To keep performance tracking straightforward, HSB negotiates to pay five times the high-water mark for any annual EBITDA generated by TWM during a three year earn-out period in excess of the $7 million run-rate established during the negotiation. It is an unusual earn-out arrangement, but the seller is compensated if AUM is significantly enhanced after the transaction, whether by steady marketing appeal or strong market returns. The buyer is protected, at least somewhat, from the potentially temporary nature of any upswing in profitability by paying a lower multiple for the increase than might normally be paid for an RIA. As long as the management of TWM can produce at least $6 million more in EBITDA in any one of the three years following the transaction date, the buyer will pay the full earn-out. Any lesser increase in EBITDA is to be pro-rated and paid based on the same 5x multiple.
- The earn-out agreement is executed in conjunction with a purchase agreement, operating agreement, and non-competition/non-solicitation agreements which specify compensation practices, reporting structures, and other elements to govern post-transaction behavior between the bank and the wealth manager. These various agreements are done to minimize misunderstandings and ensure that both the buyer and sellers are enthusiastic participants in the joint success of the enterprise.
As the earn-out is negotiated, buyer and seller run scenarios of likely performance paths for TWM after the transaction to see what the payout structure will look like per the agreement. This enables both parties to value the deal based on a variety of outcomes and decide whether pricing and terms are truly satisfactory.
Conclusion: Earn-Outs are Interactive With the Value of RIAs
Risk is an unavoidable part of investing. While we might all desire clairvoyance, it would only work if we were the sole investors who could see the future perfectly. If everyone’s forecasts were proven accurate, assets would all be priced at something akin to the risk free rate with no premium return attached. Uncertainty creates opportunity for investors, because opportunity is always a two way street.
Pricing uncertainty is another matter altogether. Not everyone “believes” in CAPM, or at least maybe not the concept of beta, but most agree that the equity risk premium exists to reconcile the degree of un-likelihood for the performance of a given asset with the value of that security. In an ideal world, a reasonable cash flow projection and a reasonable cost of capital will yield a reasonable indication of value.
In the vacuum-sealed world of fair market value, we can reconcile discordant outlooks with different cash flow projections. The differing projections can then be yoked together into one conclusion of value by weighing them relative to probability. The discount rate used in the different projection models captures some of the risk inherent in the cash flow, and the probability weights capture the remainder of the uncertainty. In a real world transaction, however, buyers want to be paid based on their expectations if proven right, and sellers also want to be paid if outcomes comport with their projections. With no clear way to consider the relative likelihood of each party’s expectations, no one transaction price will facilitate a transaction. Risk and opportunity can often be reconciled by contract, however, by way of contingent consideration.
 RIA Valuation Insights
RIA Valuation Insights