Out of the Crude Abyss
It has been almost a year since crude prices went into the abyss on last April 20th. What a day that was: OPEC’s shoe had already dropped, and the realities of COVID-19’s short term consequences panicked the global oil market into a historic backlog. Crude tankers were stranded on the seas, storage filled up, and for a short while production had nowhere to go.
The havoc wreaked on markets was severe. Demand was projected to drop between 20% and 35% by some (consumption actually dropped about 22% per the EIA). Reserve lives for some major producers dropped by around 10 years and between them reported losses north of $60 billion in 2020. To be fair, there are a couple of ways to look at this: one is a market decline in interest in these commodities; another could be rooted in the demand from investors for more nimble balance sheets coupled with the growing ability to develop acreage relatively quickly. Beyond the decline of reserves, (both through production decline and economic characterization), the bankruptcy casualty counts also skyrocketed as I have discussed before. According to the latest Haynes & Boone data, the count was 35 new bankruptcies in the second and third quarters of 2020 and over $50 billion in total debt going into bankruptcy for the full year.
What a difference a year makes.
Recently WTI closed at over $63, and it has spent most of the past month at or above $60. Many analysts now predict oil to stay in the $60’s (or higher) for the rest of 2021 (EIA on the other hand projects the mid-$50’s). It appears that low prices may have been a cure for low prices. The Dallas Fed came out with their quarterly Energy Survey a few weeks ago and its results were quite shocking to many. Its business activity index was at its highest reading ever in the five-year history of the survey.
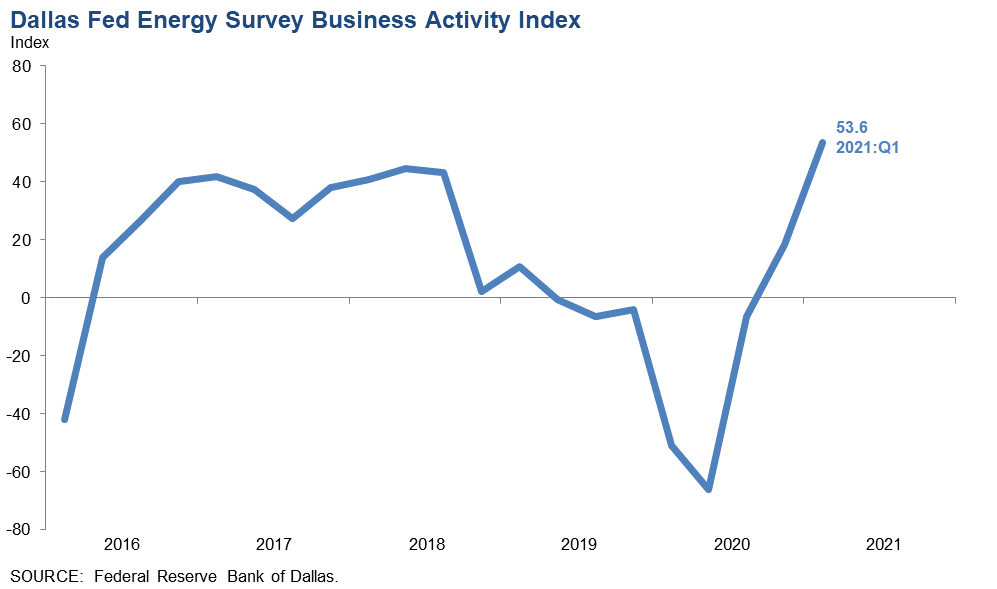
Guarded optimism among industry players is creeping back into the picture: “We are optimistic that we will have a weaning of excess oil supply, and more importantly, suppliers of oil and gas, that will lead to a slightly higher sustainable price.” said a respondent to the Dallas Fed. The S&P’s SPDR Oil and Gas Production ETF which dropped to around $30 (split adjusted) in March 2020 is now trading around $80. Production and CapEx spending are emerging as well in response to rising demand. Global oil demand and supply are moving towards balance in the second half of this year, per the IEA’s latest monthly report. In fact, producers may then need to pump a further 2 million bbl/d to meet the demand. OPEC, which has been withholding supply in tandem with other producers including Russia, this week raised its forecast for global oil demand this year. OPEC expects demand to rise by 70,000 bbl/d from last month’s forecast and global demand is likely to rise by 5.95 million bbl/d in 2021, it said.
Upstream Economics: Back In Black
It must be relieving to be “let loose from the noose” of low prices. A lot of producers should be singing AC/DC nowadays. It is now profitable to drill a lot more wells than a year ago. Heck, back then existing wells were not profitable, much less undrilled ones. In terms of reserve metrics, I have said before that value erosion usually starts at the bottom categories of a reserve report and moves upwards. Value accretion moves in reverse. The increased pricing is making larger swaths of reserves economic again.
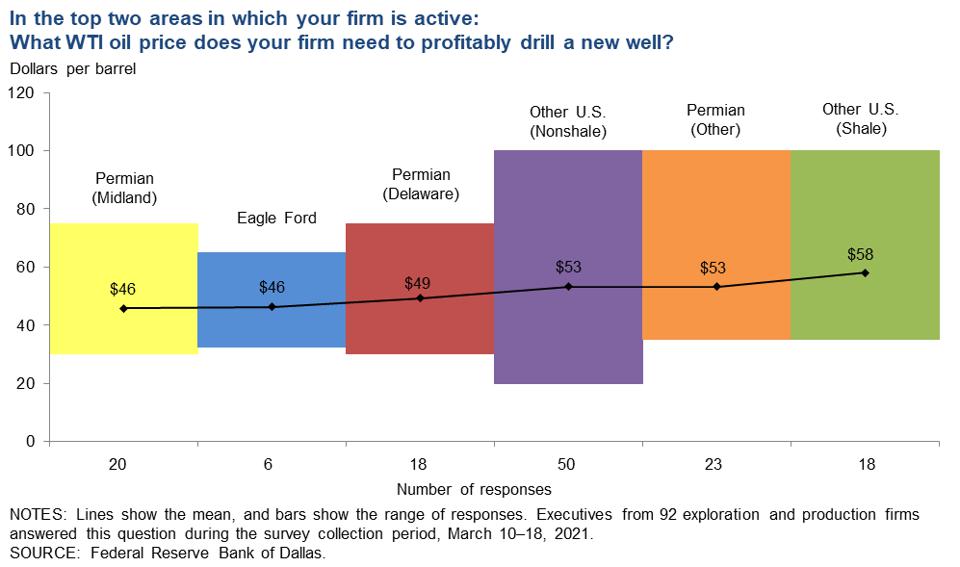
Even so, one thing that is different this time around may be the cautiousness of investors and producers to jump back on the drill bit right away. Investors have already been pulling valuations down as their standard tilted more towards shorter term returns as opposed to longer term reserves. Additionally, the Fed Survey was littered with comments expressing concern about the Biden administration’s policies being more aggressive towards regulation and ESG, thus promoting caution for aggressive drilling. In fact, the American Petroleum Institute (of all organizations) is now considering carbon pricing frameworks. Lastly, OPEC+ could yank the rug out from shale producers again if they are perceived as ramping up too quickly, according to Pioneer’s CEO. (It is notable though that Pioneer just bought West Texas producer DoublePoint for $6.4 billion. That’s approximately $30,000 per flowing barrel and $40,000 per undeveloped acre).
Next Steps
So where does this leave us? Well, in a lot better place for producers and investors than last year – that’s to be sure. The companies that have hung in this past year and made it are starting to see some improvement. That’s also good because those that utilized PPP money have been in need of price help once the government subsidies ran out. In addition, with all of the attention towards electric vehicles replacing the combustion engine, we must remind ourselves that only 1% of the U.S. light fleet is EV and that light vehicles only make up 25% of crude oil use. Demand will not be chopped out from oil’s feet just yet.
Markets are fast moving and unforgiving at times, but it appears with $60+ oil prices for 2021, that the upstream business can now start to slow down, look around, and evaluate what direction to go next.
Originally appeared on Forbes.com.
 Energy Valuation Insights
Energy Valuation Insights 







