Upstream Producers Are Not Gouging–They’re Tentative. Here Are Three Reasons Why
The drumbeats have been building for a couple of months now. Finally, as commodity prices have risen and third quarter profit reports have rolled in, so have accusations of price gouging by oil and gas companies. Senator Warren recently said as much on MSNBC. She is wrong on this point, but certainly not alone by any means. Politicians have made oil companies a proverbial punching bag on numerous fronts. This is not news. They have been rhetorical targets for decades.
However, it is true that U.S. upstream producers (both oil and gas) have yet to momentously hasten new production and aggressive drilling plans. It would make sense if they did, as it speaks to the core incentives of commodity-based businesses like oil and gas. Yet the U.S. industry remains tentative and reticent. In the meantime, the market remains in backwardation marked by continuing inventory draws and increasing prices. Why? The answer is found somewhere among supply and demand dynamics, rising costs, and capital headwinds.
Supply & Demand Issues
“We are encouraged by the restraint shown by U.S. upstream operators. By restricting capital expenditure, we are healing historic overproduction of both oil and natural gas. We believe investors will be attracted back into the E&P space if, as an industry, we continue on this path for at least a year or two more to deleverage balance sheets and return capital to investors.” – Fed Survey Respondent
It was a rough 2020, but producers have turned a corner on drilling discipline, and have restrained on the drill bit compared to years past. They also deleveraged balance sheets, and where possible, returned capital to shareholders. During 2021 traffic patterns have normalized, and apart from jet fuel, demand growth has bounced back to pre-pandemic levels. It is also creeping into winter and natural gas will be in season. That’s good news.
Energy consumption is a bellwether for economic activity. However, that production discipline in both the U.S. and OPEC+ nations has resulted in crude oil inventories being 6% below the five-year average (2016-2020) overall. The Biden administration just announced a 50-million-barrel draw from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. This imbalance started in Q3 2020 and has continued since, and is helping to keep prices high, though perhaps not for too long. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects this to come back into balance by Q2 2022.
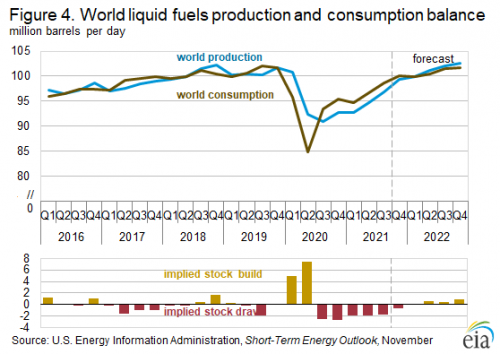
OPEC+ is slowly, but steadily adding production to the markets, while U.S. shale producers, although increasing activity, have been lagging this year. Futures markets suggest a similar outcome and prices are expected to steady according to NYMEX and EIA. As the futures curves tail out, the 60 month premium from a year ago is higher, but the near term spread is even wider, thus giving firms pause before diving in headlong with massive new production initiatives.
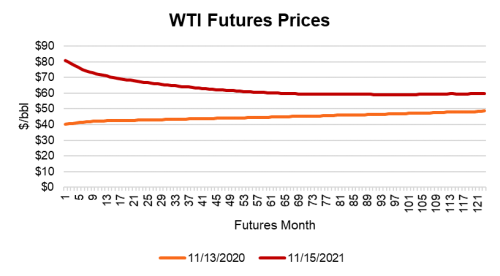
(Not all share this outlook – Bank of America sees oil at $120 by June 2022). Still, producers went through a lot to discipline themselves, and expectations by investors have been clear for years now: less drills more bills.
One other commodity that’s in demand which should impact oil and gas supply as well is the U.S. dollar. The currency is strengthening, and this brings downward pressure on prices too.
Costs
Labor is causing major problems in staffing for the increase in activity. Wages are up 20 percent, and companies are poaching employees from competitors. We are finding it difficult to increase prices to match our increase in costs. – Fed Survey Respondent
As oil and gas prices are going up, inflationary pressures are impacting the industry’s operations concurrently. The cost of oilfield services is rising quickly. Lease operating expenses are increasing. Delays are a problem as well, as 70% of the respondents to the latest Dallas Fed survey said they experienced delays of some sort in the last quarter. This is partially a result of tight labor markets and it’s dampening enthusiasm somewhat.
Also, as I have mentioned before, costs on development are going up as drilled but uncompleted (DUC) well inventories shrink. They have continued their downward march and are at the lowest levels in seven years (November 2014).
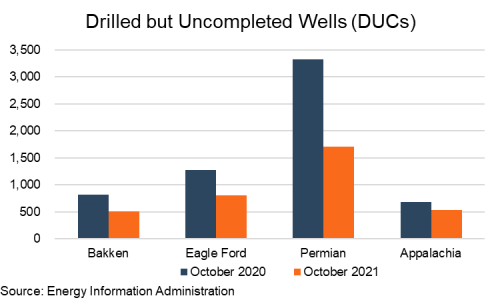
This leads to another less heralded point as well. U.S. shale oil fields have been active for around a decade now. Many of the best drilling locations have been developed. Although there are a lot remaining, they haven’t been drilled yet for a reason. Productivity per rig metrics have fallen slightly this year and it may have more to do with geology rather than technology making production growth more expensive and squeezing margins.
Investment Headwinds
“Oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids prices are greatly improved and appear to be sustainable for the coming months. The greatest headwind is skilled labor supply and access to expanding credit on our reserve base loan. Initial conversations with regional energy banks show increasing interest in advancing incremental credit. The money center banks continue to seek to reduce their commitments to oil and gas borrowers.” – Fed Survey Respondent
Although economics have shifted quickly for producers this year, though investment sentiment not so much. Capital providers are not only cautious, but fewer in number. The multi-year souring on the oil and gas sector from several investment segments has not changed recently, leaving upstream producers with fewer options.
On the debt side, some regional banks have shown a willingness to lend, but larger banks have not. Some reasons for lending discomfort have included a wariness for shale’s ability to ramp up quickly and for margins to evaporate before loans can be paid back. It’s worth a remind that U.S. production has a higher cost floor than OPEC+. Larger banks appear not to be interested.
Additionally, the shrinking pool of bankers has been mirrored by a shrinking pool of investors. Firstly, returns must be carefully evaluated as many upstream producers have hedged their portfolios and some have limited their upsides to execute their strategies. They are watching profit margins go elsewhere for the time being. Also, as ESG concepts have gained momentum, many investors have weaned their appetite off oil and gas production. There are simply fewer institutional and private equity investors evaluating and participating in the space. According to a recent Wall Street Journal article, there are less than one-third of the firms and capital available in the space compared to 2018. Simply put, it is harder for oil and gas producers to get expansion capital while they’re simultaneously paying much of it out.
Talking heads and officials may be gaining political capital while talking about gouging, price controls and the like; but in a domestic industry populated with price takers and return oriented investors, prudence and temperance are driving decision making, not their ugly cousins – greed and avarice. Thank goodness for that.
Originally appeared on Forbes.com.
 Energy Valuation Insights
Energy Valuation Insights 







