Business owners and their professional advisors are occasionally perplexed by the fact that their shares can have more than one value. This multiplicity of values is not a conjuring trick on the part of business valuation experts, but simply reflects the economic fact that different markets, different investors, and different expectations necessarily lead to different values.
Business valuation experts use the term “level of value” to refer to these differing perspectives. As shown in Exhibit 1, there are three basic “levels” of value for a business.
Exhibit 1 :: Levels of Value
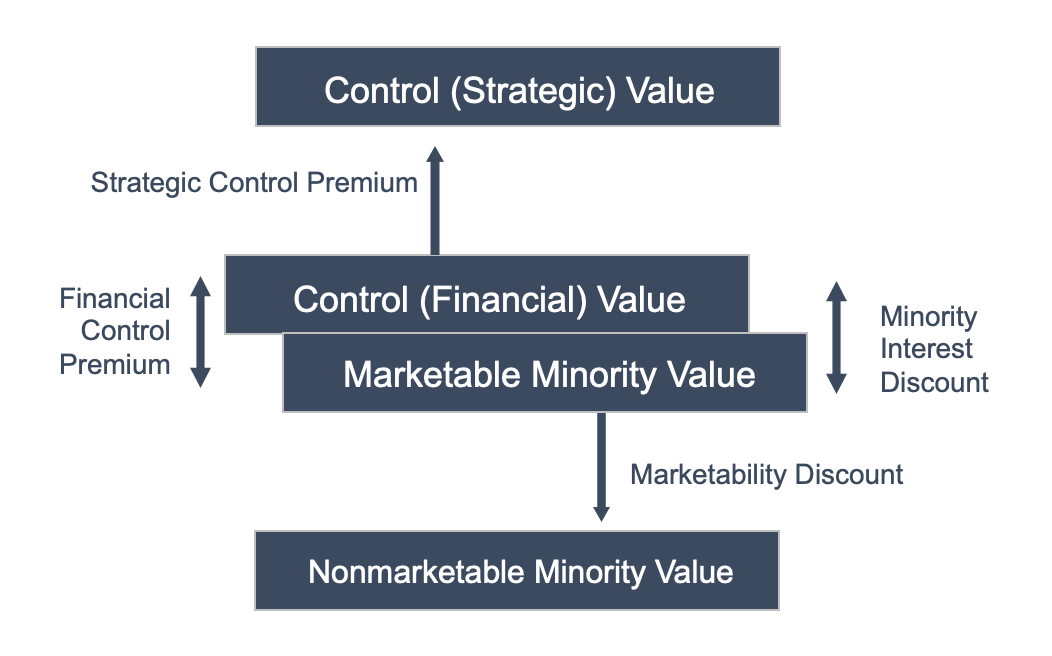
Each of the basic levels of value corresponds to different perspectives on the value of the business. In this article, we explore the relevant characteristics of each level.
Marketable Minority Level Value
The marketable minority value is a proxy for the value of a business if its shares were it publicly traded. In other words, if your business had a stock ticker, what price would the shares trade at? To answer this question, we need to think about expectations for future cash flows and risk.
Expected cash flows. Investors in public companies are focused on the future cash flows that companies will generate. In other words, investors are constantly assessing how developments in the broader economy, the industry, and the company itself will influence the company’s ability to generate cash flow from its operations in the future.
Public company investors have a lot of investment choices. There are thousands of different public companies, not to mention potential investments in bonds (government, municipal, or corporate), real estate, or other private investments. Public company investors are risk-averse, which just means that – when choosing between two investments having the same expected future cash flow – they will pay more today for the investment that is more certain. As a result, public company investors continuously evaluate the riskiness of a given public company against its peers and other alternative investments. When they perceive that the riskiness of an investment is increasing, the price will go down, and vice versa.
So, when a business appraiser estimates the value of a business at the marketable minority level of value, they are focused on expected future cash flows and risk. They will estimate this value in two different ways.
Using an income approach, they create a forecast of future cash flows, and based on the perceived risk of the business, convert those cash flows to present value, or the value today of cash flows that will be received in the future.
Using a market approach, they identify other public companies that are similar in some way to your family business. By observing how investors are valuing those “comps,” they estimate the value of the shares in the business.
While these are two distinct approaches, at the heart of each is an emphasis of the cash flow-generating ability and risk of the business.
We started with the marketable minority level of value because it is the traditional starting point for analyzing the other levels of value.
Control Level of Value
In contrast to public investors who buy small minority interests in companies, acquirers buy entire companies (or at least a large enough stake to exert control). Acquirers are often classified as either financial or strategic.
Financially-motivated acquirers often have cash flow expectations and risk assessments similar to those of public market investors. As a result, the control (financial) level of value is often not much different from the marketable minority level of value, as depicted in Exhibit 1.
Strategic acquirers, on the other hand, have existing operations in the same, or an adjacent industry. These acquirers typically plan to make operational changes to increase the expected cash flows of the business relative to stand-alone expectations (as if the company were publicly traded).
The ability to reap cost savings or achieve revenue synergies by combining your family business with their existing operations means that strategic acquirers may be willing to pay a premium to the marketable minority value. Of course, selling the business to a strategic acquirer means that the business effectively ceases to exist. The name and branding may change, employees may be downsized, and production facilities may be closed.
Nonmarketable Minority Level of Value
While strategic acquirers may be willing to pay a premium, the buyer of a minority interest in a business that is not publicly traded will generally demand a discount to the marketable minority value. All else equal, investors prefer to have liquidity; when there is no ready market for an asset, the value is lower than it would be if an active market existed.
What factors are investors at the nonmarketable minority level of value most interested in? First, they care about the same factors as marketable minority investors: the cash-flow generating ability and risk profile of the business. But nonmarketable investors have an additional set of concerns that influence the size of the discount from the marketable minority value.
Expected holding period. Once an investor buys a minority interest in a business, how long will they have to wait to sell the interest? The holding period for the investment will extend until (1) the shares are sold to another investor or (2) the shares are redeemed by the business, or (3) the business is sold. The longer an investor expects the holding period to be, the larger the discount to the marketable minority value.
Expected capital appreciation. For most businesses, there is an expectation that the value of the business will grow over time. Capital appreciation is ultimately a function of the investments made by the business. Public company investors can generally assume that investments will be limited to projects that offer a sufficiently high risk-adjusted return. Business shareholders, on the other hand, occasionally have to contend with management teams that hoard capital in low-yielding or non-operating assets, which reduces the expected capital appreciation for the shares. All else equal, the lower the expected capital appreciation, the larger the discount to the marketable minority value.
Interim distributions. Does the business pay dividends? Interim distributions can be an important source of return during the expected holding period of uncertain duration. Interim distributions mitigate the marketability discount that would otherwise be applicable.
Holding period risk. Beyond the risks of the business itself, investors in minority shares of public companies bear additional risks reflecting the uncertainty of the factors noted above. As a result, they demand a premium return relative to the marketable minority level. The greater the perceived risk, the larger the marketability discount.
Conclusion
The so-called “levels” of value reflect the real-world concerns of different investors in different circumstances. It is important for family law attorneys and their clients to understand the levels of value. When business appraisers are called upon to value a business in a divorce engagement, they will reference the levels of value. The more family law attorneys understand basic valuation concepts, the better guidance you can provide to your clients.