Additional Considerations for Your Buy-Sell Agreement
Following up on last week’s post (Three Considerations for Your RIA’s Buy-Sell Agreement), we offer four additional considerations that you should be addressing in your firm’s buy-sell agreement. We’ve seen each of these issues neglected before, which usually doesn’t end well for at least one of the parties involved. A well-crafted buy-sell should clearly acknowledge these considerations to avoid shareholder disputes and costly litigation down the road. We highly recommend taking another look at your buy-sell agreement to see if these issues are addressed before something comes up.
1. Formula Pricing, Rules-Of-Thumb, and Internally Generated Valuation Metrics Don’t Withstand Time
Since valuation is usually the most time consuming and expensive part of administering a buy-sell agreement, there is a substantial incentive to try to shortcut that part of the process. However, non-professional valuation methods, such as formula pricing, rules-of-thumb, and internally generated valuation metrics are often key reasons for costly disputes or disruptions down the road. The investment management space is particularly fraught, and not too long ago, investment manager valuations were thought to gravitate toward about 2% of AUM.
We have written extensively about the fallacy of formula pricing. No multiple of AUM, revenue, or cash flow can consistently estimate the value of an interest in an investment management firm. A multiple of AUM (typically expressed in percentage terms) does not consider relative differences in stated or realized fee schedules, client demographics, trends in operating performance, current market conditions, compensation arrangements, profit margins, growth expectations, regulatory compliance issues, and a host of other issues which have helped keep our valuation practice gainfully employed for decades.
The example below demonstrates the problematic nature of this particular rule of thumb for two investment management firms of similar size, but widely divergent fee structures and profit margins.

Both Firm A and Firm B have the same AUM. However, Firm A has a higher realized fee than Firm B (100 bps vs 40 bps) and also operates more efficiently (25% EBITDA margin vs 10% EBITDA margin). The result is that Firm A generates $2.5 million in EBITDA versus Firm B’s $400 thousand despite both firms having the same AUM. The “2% of AUM” rule of thumb implies an EBITDA multiple of 8.0x for Firm A—a multiple that may or may not be reasonable for Firm A given current market conditions and Firm A’s risk and growth profile – but which is nevertheless within the historical range of what might be considered reasonable. The same “2% of AUM” rule of thumb applied to Firm B implies an EBITDA multiple of 50.0x – a multiple which is unlikely to be considered reasonable in any market conditions.
Flawed ownership models eventually disrupt operations which works to the disservice of owners, employees, and clients.
We’ve seen rules of thumb like the one above appear in buy/sell agreements and operating agreements as methods for determining the price for future transactions among shareholders or between shareholders and the company. The issue, of course, is that rules of thumb do not have a long shelf life, even if they made perfect sense at the time the document was drafted. If value is a function of company performance and market pricing, then both of those factors have to remain static for any rule-of-thumb to remain appropriate. This circumstance, obviously, is highly unlikely.
But the real problem with short cutting the valuation process is credibility. If the parties to a shareholder’s agreement think the pricing mechanism in the agreement isn’t robust, then the ownership model at the firm is flawed. Flawed ownership models eventually disrupt operations which works to the disservice of owners, employees, and clients.
2. Don’t Forget to Specify the “As Of” Date for Valuation
This seems obvious, but the date appropriate for the valuation matters. If the buy-sell agreement specifies that value is established on an annual basis (something we highly recommend to manage expectations and avoid confusion), then the date might be the calendar year end. If, instead of having annual valuations performed, you opt for an event-based trigger mechanism in your buy-sell, there is a little more to think about.
Consider whether you want the event precipitating the transaction to factor into the value. If so, prescribe that the valuation date is some period of time after the event giving rise to the subject transaction. This can be helpful if a key shareholder passes away or leaves the firm, and there is concern about losing clients as a result of the departure. After an adequate amount of time, the impact on firm cash flows of the triggering event becomes apparent. If, instead, there is a desire to not consider the impact of a particular event on valuation, make the as-of date the day prior to the event, as is common in statutory fair value matters.
3. Appraiser Qualifications: Who Will Perform the Valuation?
Once you decide to engage a professional to value your firm, you’ll need reasonable criteria to decide whom to work with. Often, partners in investment management firms feel they are equipped to value their own business as investment management firms (unlike many other closely held businesses) have ownership groups with ample training in relevant areas of finance that enable them to understand financial statement analysis, cash flow forecasting, and market pricing data.
What insiders lack, however, is the arms’ length perspective to use their technical skills to determine an unbiased result. Many business owners suffer from familiarity bias and the so-called “endowment effect” of ascribing more value to their business than what it is actually worth simply because it is well-known to them or because it is already in their possession. On the opposite end of the spectrum, some owners are prone to forecast extreme mean reversion such that they discount the outperformance of their business and anticipate only the worst.
Partners with a strong grounding in securities analysis and portfolio management have a bias to seeing their business from the perspective of intrinsic value, which can limit their acceptance of certain market realities necessary to price the business at a given time. In any event, just as physicians are cautioned not to self-medicate and attorneys not to represent themselves, so too should professional investment advisors avoid trying to be their own appraiser.
Over time, we have reviewed a wide variety of work product from different types of service providers – but have generally observed that there are two types of experts available to the ownership of investment management firms: Valuation Experts and Industry Experts. These two types of experts are often seen as mutually exclusive, but you’re better off not hiring one to the exclusion of the other.
Valuation experts can do better work for clients if they specialize in a type of valuation or a particular industry.
There are plenty of valuation experts who have the appropriate training and professional designations, understand the valuation standards and concepts, and see the market in a hypothetical buyer-seller framework. The two primary credentialing bodies for business valuation are the American Society of Appraisers (ASA) and the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). The former awards the Accredited Senior Appraiser designation, or ASA, and the latter the Accredited in Business Valuation, or ABV, designation. Both require extensive education and testing to become credentialed, along with continuing education. Also well known in the securities industry is the Chartered Financial Analyst designation issued by the CFA Institute. While it is not directly focused on valuation, it is a rigorous program in securities analysis.
There are also a number of industry experts who are long-time observers and analysts of the industry, who understand industry trends, and who have experience providing advisory services to investment management firms.
However, business valuation practitioners are often guilty of shoehorning RIAs into generic templates, resulting in flawed valuation conclusions that don’t square with market realities. By contrast, industry experts are frequently guilty of a lack of awareness concerning the use and verification of unreported market data, the misapplication of valuation models, and not understanding the reporting requirements of valuation practice.
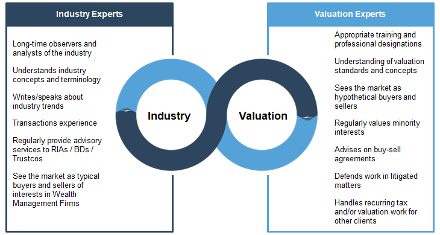
We think it is most beneficial to be both industry specialists and valuation specialists.
The valuation profession is still, for the most part, populated with generalists. But as the profession matures, an increasing number of analysts are realizing that it isn’t possible to be good at everything. Valuation experts can do better work for clients if they specialize in a type of valuation or a particular industry. Because our firm has specialized in valuing financial institutions since the day we opened for business in 1982, it was easy to pursue this to its logical conclusion.
Ultimately, you want an expert with both professional standards and practical experience.
4. Manage Expectations by Testing Your Agreement
No matter how well written your agreement is or how many factors you consider, no one really knows what will happen until you have your firm valued. If you are having a regular valuation prepared by a qualified expert, then you can manage everyone’s expectations such that, when a transaction situation presents itself, parties to the transaction have a reasonably good idea in advance of what to expect. Managing expectations is the first step to avoiding arguments, strategic disputes, failed partnerships, and litigation.
Annual valuations do require some commitment of time and expense, of course, but these annual commitments to test the buy-sell agreement usually pale in comparison to the time and expense required to resolve one major buy-sell disagreement. If you don’t plan to have annual valuations prepared, have your company valued anyway. Doing so when nothing is at stake will make a huge difference if you get to a situation where everything is at stake.
Most of the shareholder agreement disputes we are involved in start with dramatically different expectations regarding how the valuation will be handled. Going ahead and having a valuation prepared will help to center, or reconcile, those expectations and might even lead to some productive revisions to your buy-sell agreement.
 RIA Valuation Insights
RIA Valuation Insights 






