Most of our colleagues at Mercer Capital live in Texas or Tennessee – two states with very low tax burdens. This is not by design so much as by circumstance: our firm grew up where we already lived. Until recently, the relatively low cost of living, short commutes, and moderate climate came with a tradeoff: most of our clients are on the coasts, so regular travel away from home was a necessity.
Now that the pandemic has made geographic proximity for many meetings a non-issue, we’re beginning to wonder how many of our clients are ultimately going to join us. Dynasty’s move from New York to Florida and UBS’s relocation to Tennessee got plenty of attention. And we’re starting to hear of smaller RIAs contemplating similar moves. This isn’t a crowded trade yet though; most investment management firms still call high-cost, high-tax states home.
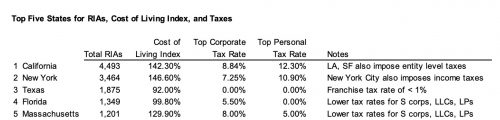
Texas and Florida have been climbing the rankings of states with the most RIAs, but two states still dominate this survey – New York and California. New York’s position is even stronger if you include adjacent communities of investment management firms in Connecticut, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
California is in an enviable position as the fifth largest economy on the globe, not to mention mostly-beautiful weather. That hasn’t been enough for Schwab, which has been migrating staff to Texas, Colorado, and Arizona for years. Now we’re starting to hear from California clients with staff members who moved out of state during the worst of the pandemic and would like to continue working remotely. When will their employers follow?
Manhattan is another story altogether, with city tax burdens layered on top of state taxes. With all due respect to Manhattan’s theme song, in the post-pandemic, remote-work world, if you can make it anywhere, why make it there? We have another wealth management client who just relocated from New York to Tennessee – cost structure and concern over the quality of life in Manhattan for the foreseeable future were key factors.
What the table above doesn’t show is the value of the talent pools already established in financial hubs like San Francisco and New York. But the relative cost of living may be enough to convince some of that talent to relocate. If that becomes a trend, all bets are off.
The wrong corporate structure can exacerbate the state tax differential. Imagine the extreme scenario of a Manhattan based C Corporation that considers moving to Florida and converting to an LLC.
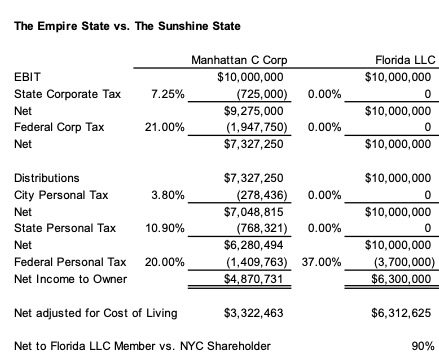
After-tax dividends/distributions to the Florida LLC member are about 30% higher than for a shareholder in a New York City C Corporation with the same EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes). But this differential is far greater if you consider the cost of living in Florida versus New York – a difference that will widen further if President Biden successfully rolls back some or all of the reduction in corporate taxes enacted in 2017.
As for proximity to clients, there are reasons to expect ultra-high net worth families in California and New York to relocate. Florida still has no estate tax, while New York just raised theirs. Tennessee and Texas (two states with no personal income tax) also have no estate tax, and Tennessee has strong and well-developed trust laws considered on-par with South Dakota.
Anecdotal experience supports this trend. Friends on the west coast and in the northeast have told me they have a recurring conversation with their neighbors that revolves around the question: “how much longer are you going to stay here?” The implication of this question is that, as soon as they could, they would decamp for a lower-tax, lower-cost of living part of the U.S. Just as the pandemic accelerated many trends, we expect to see a migration of wealthy clients to more cost-effective jurisdictions, as well as the firms that serve them.


